31 Oct What Is a Laser Engraving Machine?
Jump To:
- What Is a Laser Engraving Machine?
- How Does Laser Engraving Work?
- Common Applications of a Laser Engraving Machine
- What Is the Engraving Process on the Machines?
- How Long Does It Take to Laser Engrave?
- Will an Engraving Wear Off?
- What Do You Need for Laser Engraving?
- Take a Look at Our Laser Marking and Engraving Machines
Laser engraving using a laser engraving machine creates permanent marks in a material so manufacturers and customers can easily identify and track the product. Manufacturers use laser engraving to create product identification numbers, barcodes and other marks on materials like metal, wood and plastics. These marks can withstand time and rugged use, making them ideal for industries like automotive manufacturing and medical device production.
If you’re considering using laser engraving in your operations, it’s critical to understand how laser engraving machines work. Then you can select the equipment that best suits your needs.
What Is a Laser Engraving Machine?
A laser engraving machine is a piece of equipment that performs laser engraving, which is the process of engraving designs, letters or numbers on materials using a laser beam. These engraving machines use automation to achieve precise cuts and engravings on various materials, including metal, wood, glass and plastic. The essential parts of a laser engraving machine are the laser and the lenses, which create and concentrate a beam of light powerful enough to engrave the design.
There are many uses of a laser engraving machine. Laser engraving provides durable, long-lasting marks like:
- 2D data matrix codes
- Barcodes
- QR codes
- Logos
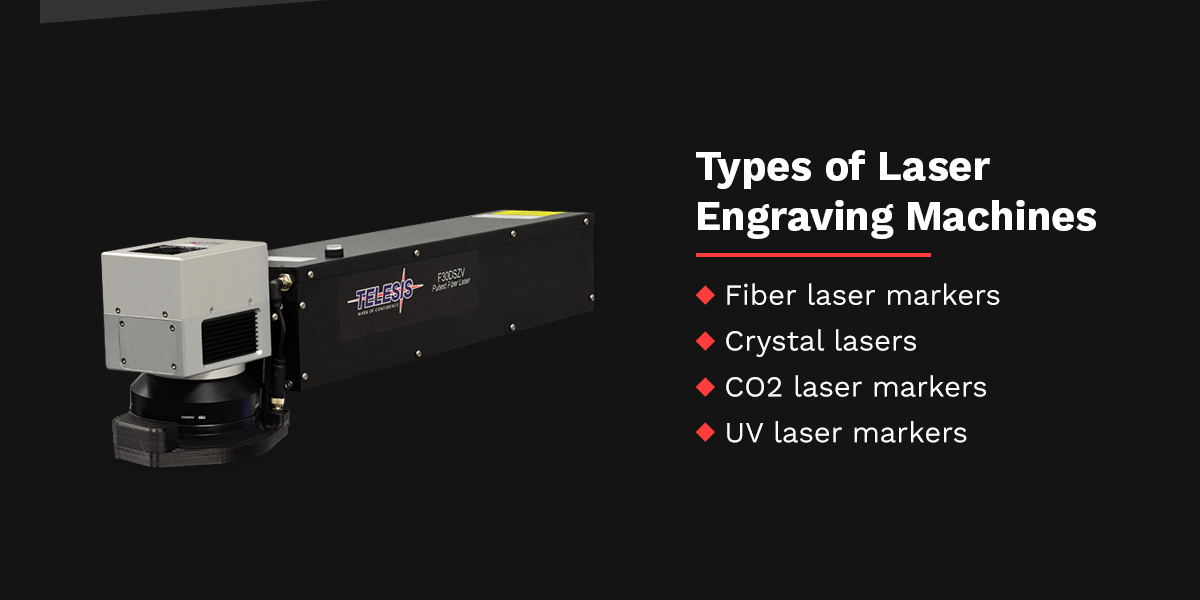
Types of Laser Engraving Machines
Many types of laser engraving machines are available. These engraving machines function differently, making them suited for various applications. The most common types of laser engraving machines are:
- Fiber laser markers: A fiber laser marker is a laser engraving machine that conducts electricity using glass fibers. A laser diode creates the light and moves it along a fiber-optic cable, where it gathers energy and changes shape to fit the application. Fiber laser markers make precise markings and are extremely powerful. Learn more in our blog post about what fiber laser markers do.
- Crystal lasers: Engraving machines with crystal lasers use garnet or vanadate crystals to change the beam’s characteristics and give it exceptionally high power. For example, vanadate laser markers provide improved beam quality and depth of focus over fiber laser markers.
- CO2 laser markers: This laser engraving machine directs the emitted light through glass tubes containing gases like carbon dioxide (CO2), helium, nitrogen and hydrogen. These CO2 laser marking machines bounce the light between two mirrors as it grows in intensity. CO2 laser markers are versatile machines and work well with materials like plastic and wood.
- UV laser markers: These laser engraving machines use ultraviolet (UV) light to mark materials using cold marking methods. Manufacturers can create minimal heat damage on organic materials and plastic with UV laser markers.
How Does Laser Engraving Work?
Laser engraving works by using a laser beam to focus a high amount of heat onto a surface to form a pattern. The super-focused laser uses concentrated heat to cut at a certain depth, removing the material’s top layer. Laser engraving machines are programmable to engrave the material with designs, including writing, numbers and patterns like logos. These markings are permanently imprinted into the material, making them durable even after harsh use.
This process owes its existence to recent advances in laser technology. The word laser is an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. Laser engraving machines repeatedly concentrate light beams until they reach the correct power level. The different types of laser engraving machines use varying methods to excite the electrons in the beam to generate high enough energy for the laser to cut the material. Using a laser for engraving requires three factors to operate correctly:
- Concentration: Laser engraving machines must focus the wavelengths of light very close together to increase the beam’s power. The process of concentration enables the light to focus on a single point.
- Energy: Once concentrated, the laser must gather enough energy to change the material’s surface from a solid to a gas, a process called sublimation. Sublimation requires extremely high temperatures to engrave the material, especially harder materials like metals.
- Direction: Finally, the laser engraving machine directs the beam’s course to mark letters, numbers and designs. The laser’s movement must be precisely controlled to ensure accuracy.
Laser engraving is ideal for improved product identification and tracking. Printed product labels are easily lost or damaged, and other forms of engraving, like handstamps, can be dangerous to operate. Laser engraving makes it easier to identify and track products by permanently marking the material with a durable design that’s human- and machine-readable.
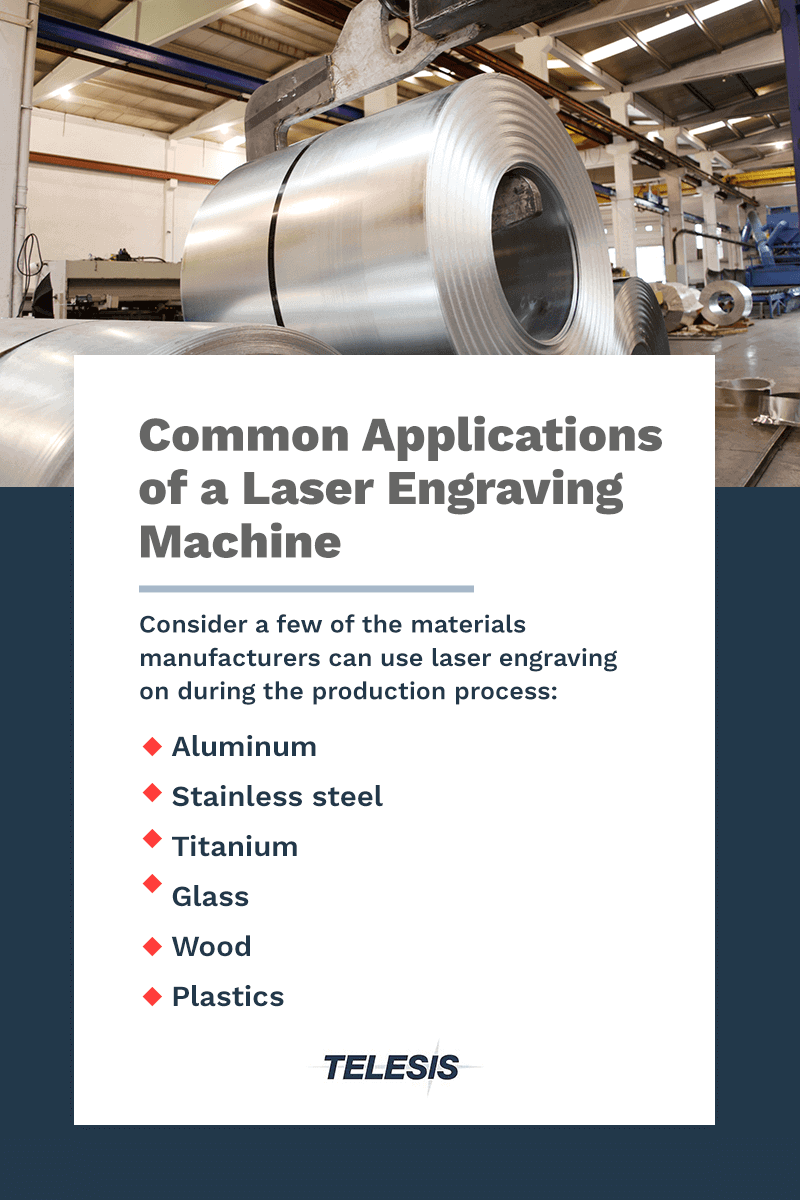
Common Applications of a Laser Engraving Machine
Laser engraving machines are used in various applications and with different materials. From marking serial numbers on medical device parts to engraving certifications on an aerospace component, laser engraving is a highly versatile technique. Consider a few of the materials manufacturers can use laser engraving on during the production process:
- Aluminum: Laser engraving on aluminum is prevalent in the automotive and defense industries, where manufacturers must permanently mark various components for identification. You can use many laser engraving machines on aluminum, including fiber, UV and vanadate laser markers.
- Stainless steel: Any grade of stainless steel can be laser engraved. Various laser settings allow manufacturers to change the steel’s surface color without affecting the structural integrity. Fiber and UV laser markers are powerful enough for this material.
- Titanium: Titanium is a popular material in the aerospace and defense industry because it’s lightweight yet incredibly sturdy. Aircraft manufacturers use titanium to construct aircraft engines and frames. You can use nearly any laser engraving machine for titanium, from fiber laser markers to UV laser engraving machines.
- Glass: Using a laser engraving machine with glass can be a challenge since glass is a delicate material. It’s essential to use a laser engraving machine adequately suited to the task. A CO2 or UV laser marker works best with glass since these laser engraving machines operate at high speeds and prevent glass fracturing. You can carve designs on flat or curved glass workpieces using laser engraving.
- Wood: Another popular application is laser engraving on wood. Manufacturers should know that only CO2 laser markers are safe for wood since fiber lasers can pose a fire hazard and usually create uneven marks.
- Plastics: Many manufacturers also require permanent markings on plastic components, like parts made from acrylic and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). CO2 and UV laser markers are ideal for these applications because they prevent scratching.
What Is the Engraving Process on the Machines?
The laser engraving process is when the machine cuts a design into a material’s surface. Although this process can vary depending on the engraving machine, it follows a few general steps. Check out this overview of the laser engraving process to learn more about how these machines work:
1. The Operator Enters the Design
Before the laser engraving machine can engrave the material, the machine operator must enter a design into the control system. Laser engraving machines use automation and computer software to translate a design like a logo or a barcode into the laser’s movements across the material’s surface. Some laser engraving machines can store hundreds of designs, making it easier for manufacturers to achieve peak efficiency.
2. The Operator Places the Object
After the laser engraving machine receives the design, the operator must put the material in the right place for engraving. Often, smaller materials can go into the laser tray. Larger workpieces may require a larger surface. Many laser engraving machines can be integrated into the production line for easier engraving.
3. The Operator Finalizes the Settings
The operator ensures the final settings on the machine are correct for the material and desired engraving pattern. The laser must focus on the workpiece. Then the operator selects the desired engraving settings, including depth and beam power. These settings will depend on the material and the operator’s chosen pattern for the laser engraving.
4. The Machine Initiates the Laser
Once the operator finalizes the machine’s settings, the machine activates the laser using software to begin engraving. The laser passes over the material throughout the engraving process, carving deep marks with a high contrast that can remain legible even under harsh conditions.
5. The Material Undergoes Processing
After the laser completes the engraving, the operator removes the material from the machine for further processing. Sublimation creates residues like metal shards and soot after removing the top layer of the material. The material must be processed to clear this residue. Some applications might use shot blasting or heat treatment to eliminate irregularities.
How Long Does It Take to Laser Engrave?
The time it takes to laser engrave depends on the material and the engraving size. The process of engraving can happen quickly. Laser engraving machines are extremely powerful and can concentrate a beam and make a cut into the material within a few seconds.
However, larger applications or harder materials might require a bit more time. Very complicated design can take as long as several minutes, depending on the engraving design, material and laser’s power. Using a higher power laser might help an engraving project go faster.
A project’s details can also affect the time it takes to laser engrave a material. If a laser engraving machine is integrated into a production line, it may be able to complete designs faster than if switching between multiple designs for different projects. Yet sometimes, unique laser engraving projects demand a unique solution. Creating a customized laser engraving machine can help you complete your projects faster and more efficiently.
Will an Engraving Wear Off?
A laser engraving will not wear off because this type of marking is a permanent cut into the material’s surface. Whereas other types of markings are merely printed on a material’s surface, laser engraving carves into the surface by removing the material’s top layer through sublimation.
Laser engraving has become so popular with manufacturers because of its permanence. Removing a laser engraving would require significant damage to the material, such as cutting the part off, sanding it down or searing it to erase the engraving. Laser engravings can endure harsh conditions, making them durable even in demanding environments.
In contrast, other product marking methods, like printed labels, can become unreadable. Ink smears and the cost of consumables like ink and paper can accumulate. Laser engraving offers benefits like permanent traceability and eliminates consumables. Making the switch from inkjet labels to laser engraving is an excellent way to ensure product identification numbers, QR codes and other markings are always legible.
Using laser engraving on the material’s surface also helps prevent counterfeiting. Laser engraving is tamper-resistant since erasing or removing the engraving would require damage to the material. The best way to ensure a laser engraving remains permanently is to use the right laser engraving machine for the material.
What Do You Need for Laser Engraving?
You need a few critical items before you can begin laser engraving projects. Here are the top things you need, whether you’re manufacturing many automotive parts or completing small-scale laser engraving projects:
1. A Laser Engraving Machine
The type of engraving machine that will work best for your application depends on several factors:
- The scale of your operation: Industrial laser engraving machines are ideal for large production quantities, but a smaller-scale laser engraving operation might prefer an entry-level laser engraving machine. These laser marking machines are compact and lightweight and could be better suited for smaller workspaces.
- Materials: Softer materials that could burn or splinter demand laser engraving machines that prevent cracking and reduce fire hazards, like CO2 and UV laser markers. Fiber laser markers are powerful enough for all kinds of metals. You may want a laser engraving machine that offers versatility.
2. A Cooling System
Some laser engraving machines require an effective cooling system to prevent the machine from overheating. During laser engraving, the laser generates heat within the machine, which could damage the machine components if it isn’t treated. Telesis laser markers use air to cool the system.
3. A Ventilation System
Laser engraving machines produce smoke, fumes and airborne debris, especially when engraving plastics. A ventilation or fume exhaust system is essential for protecting yourself, other people and the machine from the particles it produces. A good ventilation system should expel vapors, odors and dust.
4. Laser Software
Laser software is an essential component of laser engraving machines — it enables more complex patterns and streamlines the production process for system operators. Look for laser software that integrates with other manufacturing software and is user-friendly. Some software can also prevent costly mistakes by stopping the laser engraving machine if specific protocols are not met.
5. Materials
Finally, gather the materials you will use for your projects. It may take trial and error to determine the correct machine settings for each material.
Take a Look at Our Laser Marking and Engraving Machines
Our easy to use laser engraver machines are powerful pieces of equipment that can produce various cuts on a wide range of materials. Whether you’re in the automotive or medical device manufacturing industries or work out of your workshop, laser engraving makes the permanent marks you need to create, track and identify your products.
At Telesis Technologies, Inc., we manufacture state-of-the-art industrial laser marking systems that set the bar for efficiency and ruggedness. We are a one-stop shop for all your product marking needs, from laser software to custom machine design. Our team strives to provide expert service so you can focus on your operation’s core tasks.
To learn more about our equipment, view our laser marking systems. You can also contact us today to request a quote, and our team will reach out to you shortly.