Types of Laser Marking Machines for Plastic
You can use several types of laser engravers for plastics. Explore the suitable machine types we offer:

Whether you’re already in the plastic industry or looking to expand your business, laser engraving your plastic parts can reduce labor costs and help improve your return on investment. It also presents a practical way for your business to save money and time and lower its environmental impact. That’s why it’s crucial to choose the right laser equipment to ensure quality results.
Using Industry 4.0 systems like AI, robotic integration and our proprietary Merlin® software, Telesis Technologies, Inc. provides robust laser engravers for plastic that can increase your facility’s productivity.
Contact UsLaser engraving plastic has several benefits with the potential to enhance your workflow, including:
Using a laser to mark plastics lengthens your tool life and eliminates the need for costly consumables like ink.
Laser marking can be performed quickly, resulting in fast processing times.
Since the laser can be automated, marking your plastic parts will require little to no additional effort.
Permanent engraving solutions work well for many different production lines, whether you make consumer products or medical devices.
Because laser engravers require no consumables, you don’t need harmful chemicals or toxic substances to distinguish your products.

Multiple plastics are suited for laser marking, including these common formulations:
Electronic Components

Microchips

Casings

Food Packaging

Plastic Pill Bottles

Number Tags
Oil/Gas Cap
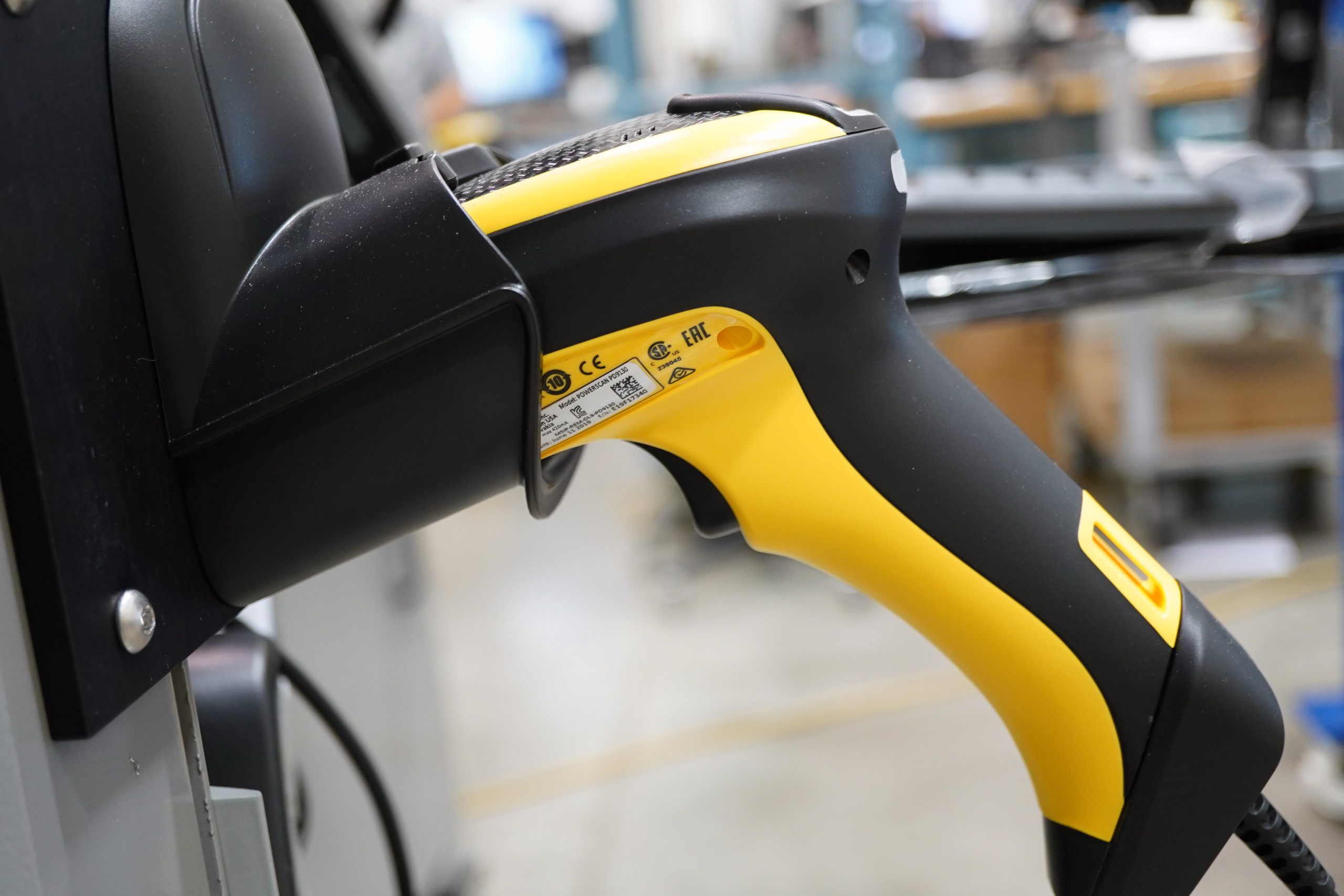

Handheld gadgets

Data Matrix Codes & QR Codes
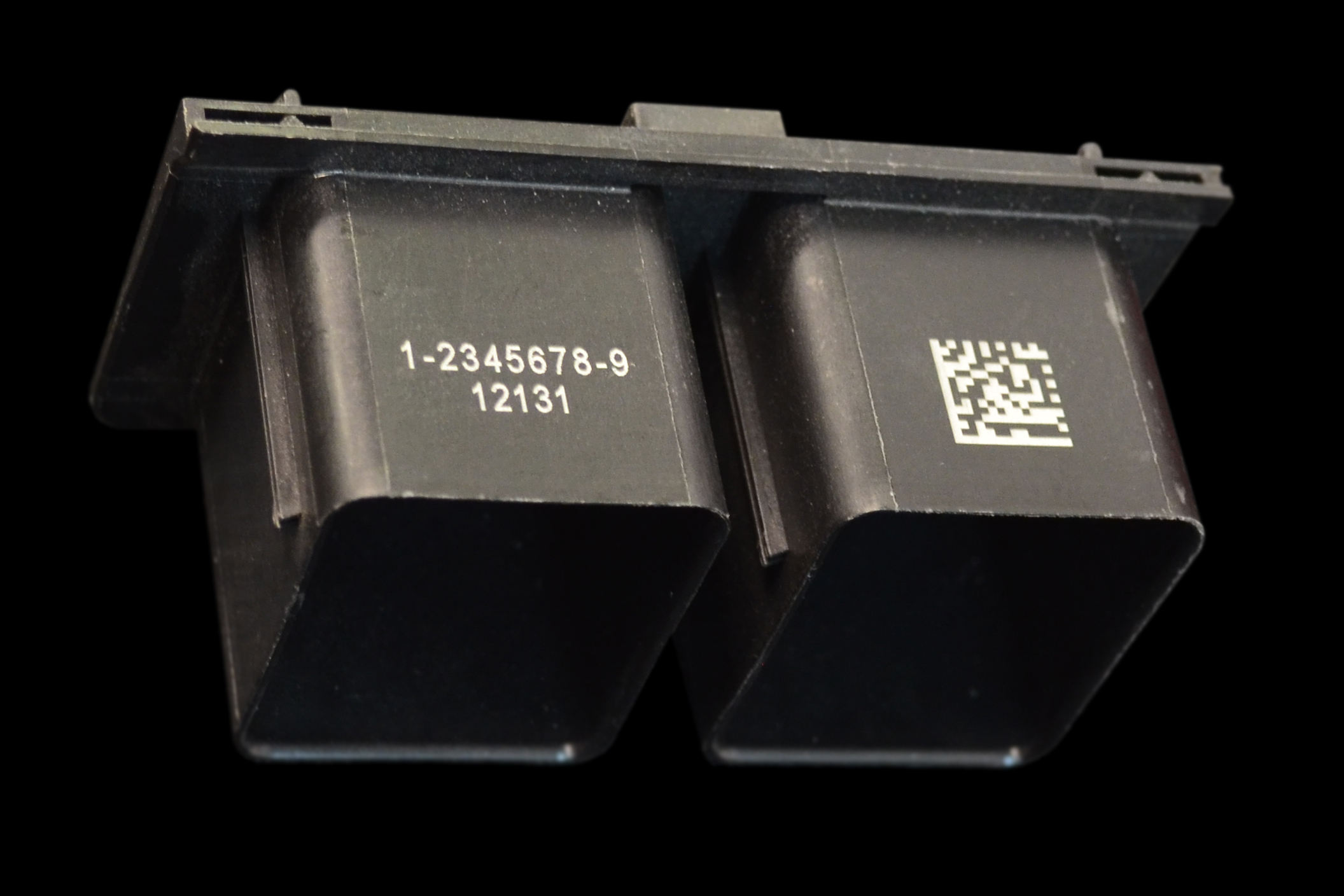

Serial Numbers & Data Matrix Codes

Barcodes & Serial Numbers

Logos
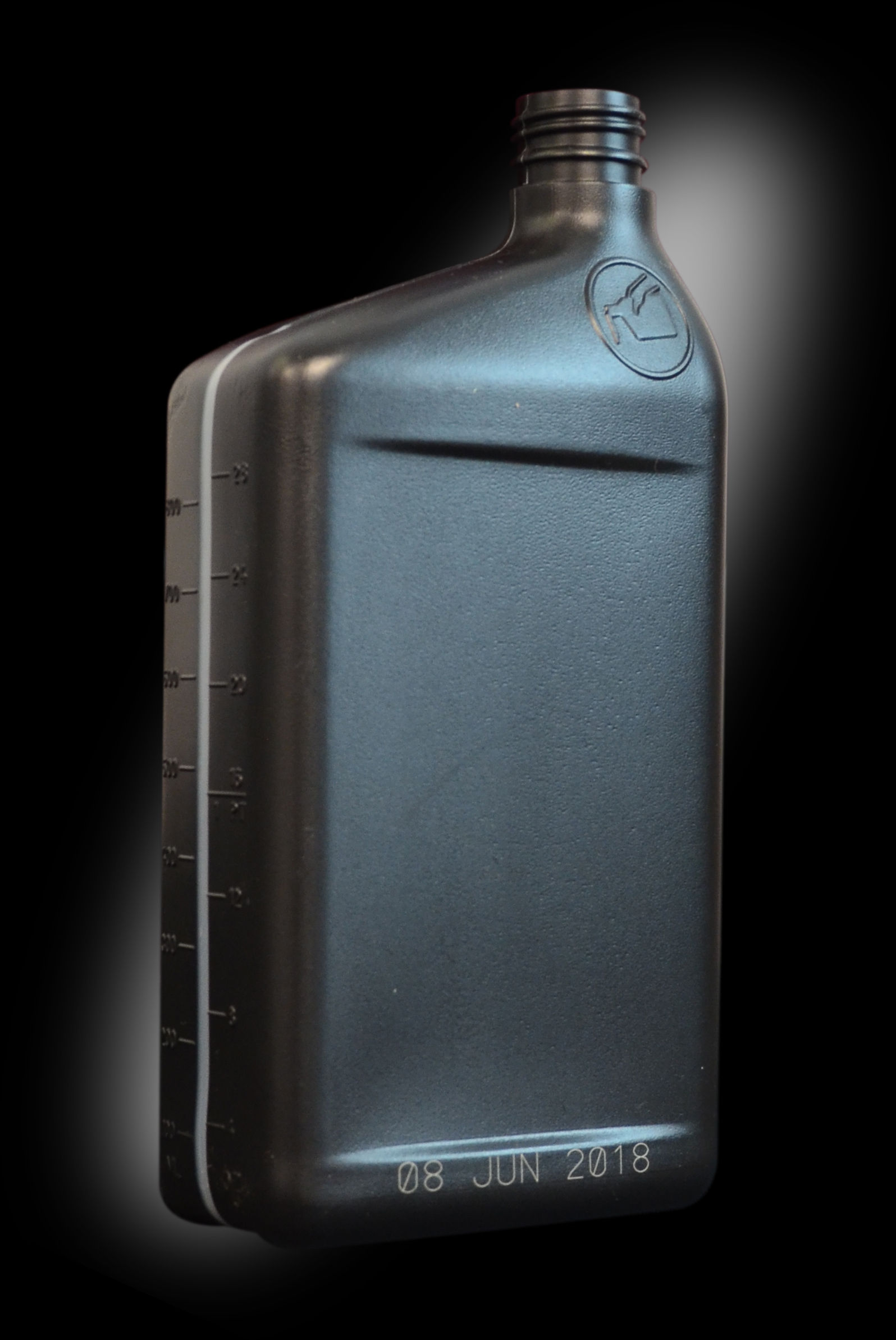

Expiration Information

Text & Product Details

Instructions & Diagrams
Volumetric Information
You can use several types of laser engravers for plastics. Explore the suitable machine types we offer:
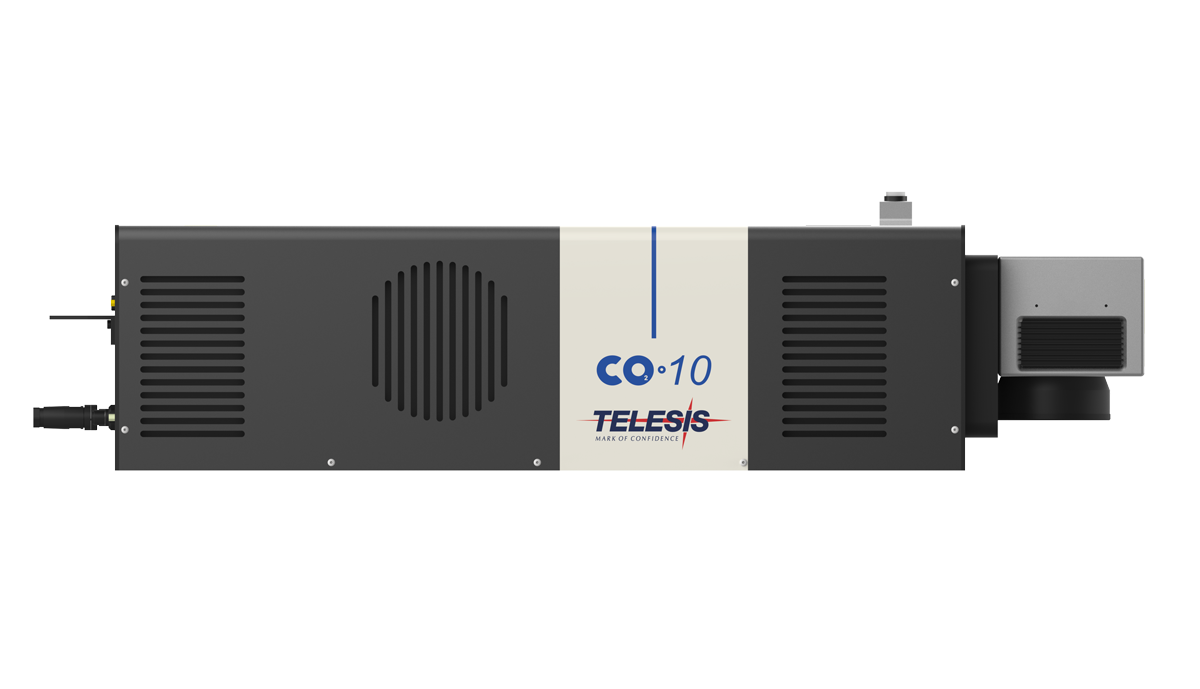

CO2 lasers are suited to general-purpose marking on metals and plastics, providing high-quality, cost-effective performance.
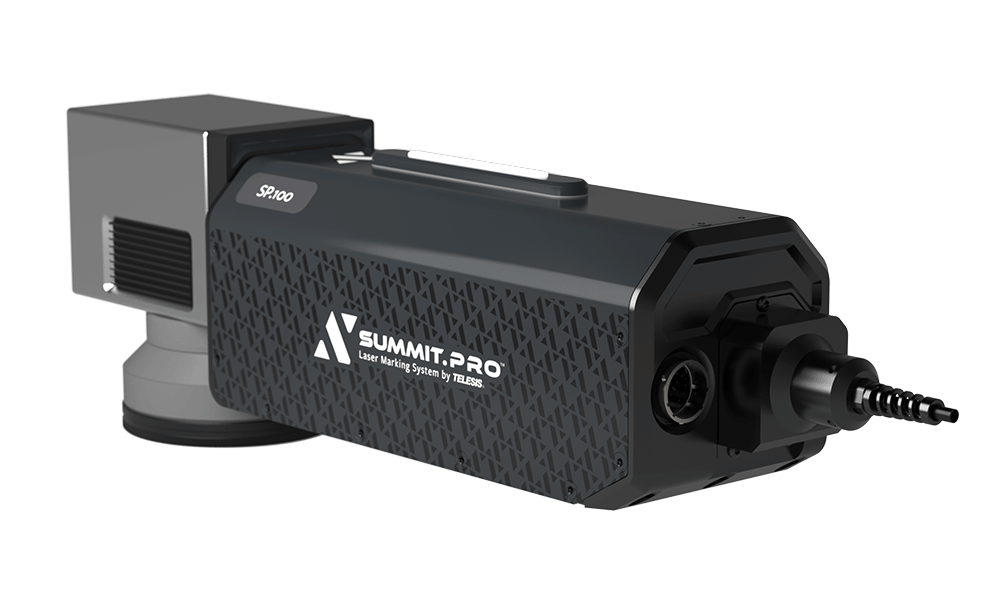

Fiber lasers cause minimal surface disruption and yield high-contrast results on many different materials.
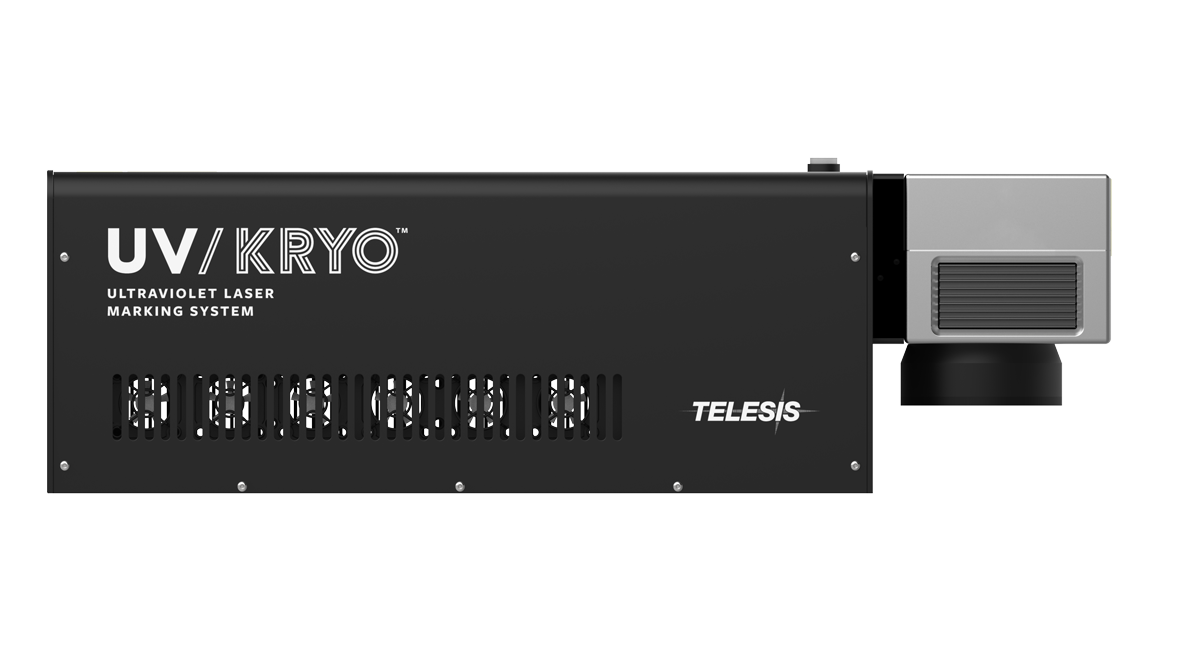

These machines create fine, high-contrast markings, ideal for heat-sensitive plastics.

Marking plastics using a laser can be accomplished in several different ways. Typical methods include:
We focus on customer satisfaction by providing reliable, easy-to-use equipment. Here’s why thousands choose us: